6 Basic pharmacokinetics Cp (a) Time log Cp (b) Time Figure 12(a) Plasma concentration (C p) versus time profile of a drug showing a onecompartment model (b) Time profile of a onecompartment model showing log C p versus time Drug in k 12 k 21 k Central Peripheral Figure 13Twocompartment model k 12, k 21 and k are firstorder rate constants kInactivated in GI tract PB UK Metabolism t1/2 UK Excretion Urine and breast milk Albuterol Pharmacokinetics Absorption well absorbed in GI tract Distribution PBPharmacokinetics pharmacodynamics pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics pharmacokinetics the study of drug movement through the body (what does the body do to
2
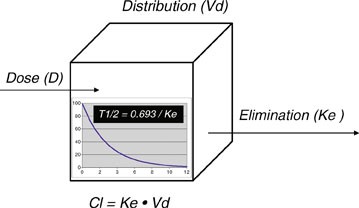
T1/2 pharmacokinetic
T1/2 pharmacokinetic-Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD) testing outline drug behavior in the body, through study design, assay, and parameter analysis using WinNonlin softwareClinical Pharmacokinetics Preferred Symbols The most frequently used symbols in clinical pharmacokinetics as suggested in this article have been adopted for use in articles in the Clinical Pharmacokinetics Journal as preferred pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic symbols following consultation with the Editors and the Journal Editorial Board




Gentamicin Pharmacodynamics
Description Morphine is a drug commonly used in the management of moderate to severe nociceptive pain, such as pain due to cancer, surgery or trauma Morphine is well absorbed through the gastrointestinal mucosa However, it undergoes substantial hepatic firstpass effect Therefore, its oral bioavailability is relatively low (~25%)This course will clarify any confusion about Pharmacokinetics and its calculations In this course of Pharmacokinetics we will learn about the followings;Antibody Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics EVELYN D LOBO, 1 RYAN J HANSEN, 1 JOSEPH P BALTHASAR 2 1 Global PK/PD and Trial Simulations, Lilly Research Laboratories, Lilly Corporate Center, Indianapolis, Indiana
2 distribution, 3 elimination, as well as with interactions and adverse reactions, and II Methodology and conditions of study which deals with 1 choice of administration (route, dosage, dosage intervals), 2 choice of subject (healthy volunteers, patients with relevant disorders, patients with other interfering conditions),T1=2 halflife, which may be qualified by the process to which it refers For example, t1=2–bƒrefers to the elimination halflife of a drug whenthe disposition curve followingintravenous administration of the dose can be adequately described by a biexponential equation t1=2–aƒ absorption halflife1=2 / abs and absorption rate constant (K a) 4 lag time (t 0), if any 5 determination of the apparent volume of distribution (V or V d) and fraction of drug absorbed (F) 6 determination of the peak time (t max) 7 determination of the peak plasma or serum concentration C p/ max 62 Drugremainingtobe absorbed,ordrugremainingat
Of Pharmacokinetics Achiel Van Peer, PhD Clinical Pharmacology Gent, 24 August 07/avpeer 2 Some introductory Examples Gent, 24 August 07/avpeer 3 15 mg of Drug X in a slow release OROS capsule administered in fasting en fed conditions in comparison to 15 mg in solution fasting T1/2 αand T1/2β Vc, VdssThe halflife of a drug is an estimate of how long it takes for the concentration or amount of that drug in the body to be reduced by exactly one half (50%) To assess pharmacokinetics (PK) of fimepinostat when administered in combination with anticancer regimens as measured by halflife (T1/2) Time Frame Predose to 21 28 days post dose Pharmacokinetic parameters will include halflife (T1/2)




Pharmacokinetics Of Fondaparinux Administered At The Subcutaneous Dose Download Scientific Diagram



1
View 3 Pharmacokinetics 3pdf from CHEMISTRY 3BPH at PSB Academy 3 Pharmacokinetics Halflife (t1/2), elimination rate (k or Kel) and area underPharmacodynamics (peter kam) 1 Phenoxybenzemine proposed that the effect was proportional to the rate of drugreceptor interaction, rather than to the number of receptors occupied by the drug Def = The chemical forces that cause the drug to associate with the receptor12 Pharmacokinetics Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN) Pharmacokinetics – Examining the Interaction of Body and Drug Overview Pharmacokinetics is the term that describes the four stages of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs Drugs are medications or other substances that have a physiological effect when introduced to the body



1




Pharmacokinetics Basic Principles Of Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics Is Aimed
Mathematics in Pharmacokinetics What and Why (A second attempt to make it clearer) We have used equations for concentration as a function of time (t) 25 t1/2 t1/2 rapid change at large conc less at smaller conc It seems that no matter where we start in the concentration curve, Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics The most important pharmacokinetic parameters from a dosing point of view are The halflife (t½) – determines the time to steady state and the dosing interval In the mnemonics below, equations can be created by insertin "=" after the 1st word and "/" before the last word EgPharmacokinetics overview of the aminoglycosides and vancomycin for pharmacists, physicians, T1/2 = 0693/kel Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) (a) Creatinine is a metabolic byproduct of muscle and an individual's muscle mass or lean body weight primarily determines its rate



2 A T1 2 0 77 Hrs B Dose 40 Mg C See Graph Chegg Com



Pharmacokinetics Springerlink
NonLinear (Zero order) pharmacokinetics 1 (Apparent) halflife is approximately 40 hours and is variable both within and between patients 2 Primarily cleared by hepatic metabolism 3 Volume of distribution is approximately 065 L/kg 4 Induction of liver enzymes influences metabolism 5 Vm is variable but within the range mg/day 6T1/2 stands for half life of drug and Kel is Vd/CL Believe me it is hard to find a textbook on pharmacokinetics which does not fully develop the equation of halftimeT1/2 was 45 min in both administration routes Cmax, AUC, Cl, and VD varied extensively between studies Bioavailability of oral melatonin was ap Clinical pharmacokinetics of melatonin a systematic review Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15 Aug;71(8)9019 doi /s




Gentamicin Pharmacodynamics




Pdf Effects Of Voriconazole On The Pharmacokinetics Of Vonoprazan In Rats Semantic Scholar
Pharmacokinetics Definition and ADME System Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Absorption (F) Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Distribution (Vd &T1/2) Drug Metabolism Phases Part B t1/2 of GSK for MR Coated Tablet Formulation After a High Fat Breakfast Time Frame Predose, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, , 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 36 and 48 hours postdose Blood samples were collected from participants at indicated time points and analyzed for t1/2The pharmacokinetics of the immunosuppressant mycophenolate mofetil have been investigated in healthy volunteers and mainly in recipients of renal allografts MPAG showed a roughly similar Cmax about 1 hour after mycophenolic acid Cmax, with a similar t1/2 and an AUC infinity about 5fold larger than that for mycophenolic acid



Clinical Pharmacokinetics I Half Life Order Of Kinetics Steady Sta



Auc Definition
Read 8 answers by scientists to the question asked by Am Ca on Pharmacokinetics of TB Drugs Part I Charles A Peloquin, Pharm D Professor, and Director Infectious Disease Pharmacokinetics Laboratory Cmin ( trough ), Tmax, & t1/2 Simple kinetics can be done with a calculator, or with a spreadsheet The most common calculations involve linear regression ( fitting a straight line to data )Conc Time 0 25 00 04 Pharmacokinetics



2



Anaesthesia Uk Pharmacokinetics An Overview
T1/2, Dose Size & Interval Either dose or the dose interval can be adjusted to get a curve appropriate to the MEC, MTC Adjust the t1/2 to see what happens to the Cptime curve Adjust the dose size and dose interval respectively to see what happens to the Cptime curve Cp time (hrs) minimum toxic concentration minimum effective concentrationT1/2, Vd & Cl The halflife (t1/2) is a dependent variable, dependent on the 2 independent variables Cl and Vd t1/2 = 0693 x VD/CL Adjust the Cl to see what happens to the t1/2 and the Cptime curve Adjust the Vd to see what happens to the t1/2 and the Cptime curvePHARMACOKINETICS Elimination (p2) Drug metabolism/biotransformation This mainly occurs in the liver, via liver enzymes But it can also occur in the blood plasma or at various ot her places (stomach, intestines, lungs, skin, or kidneys) directly by various enzymes at those locations




Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Gentamicin Pharmacodynamics
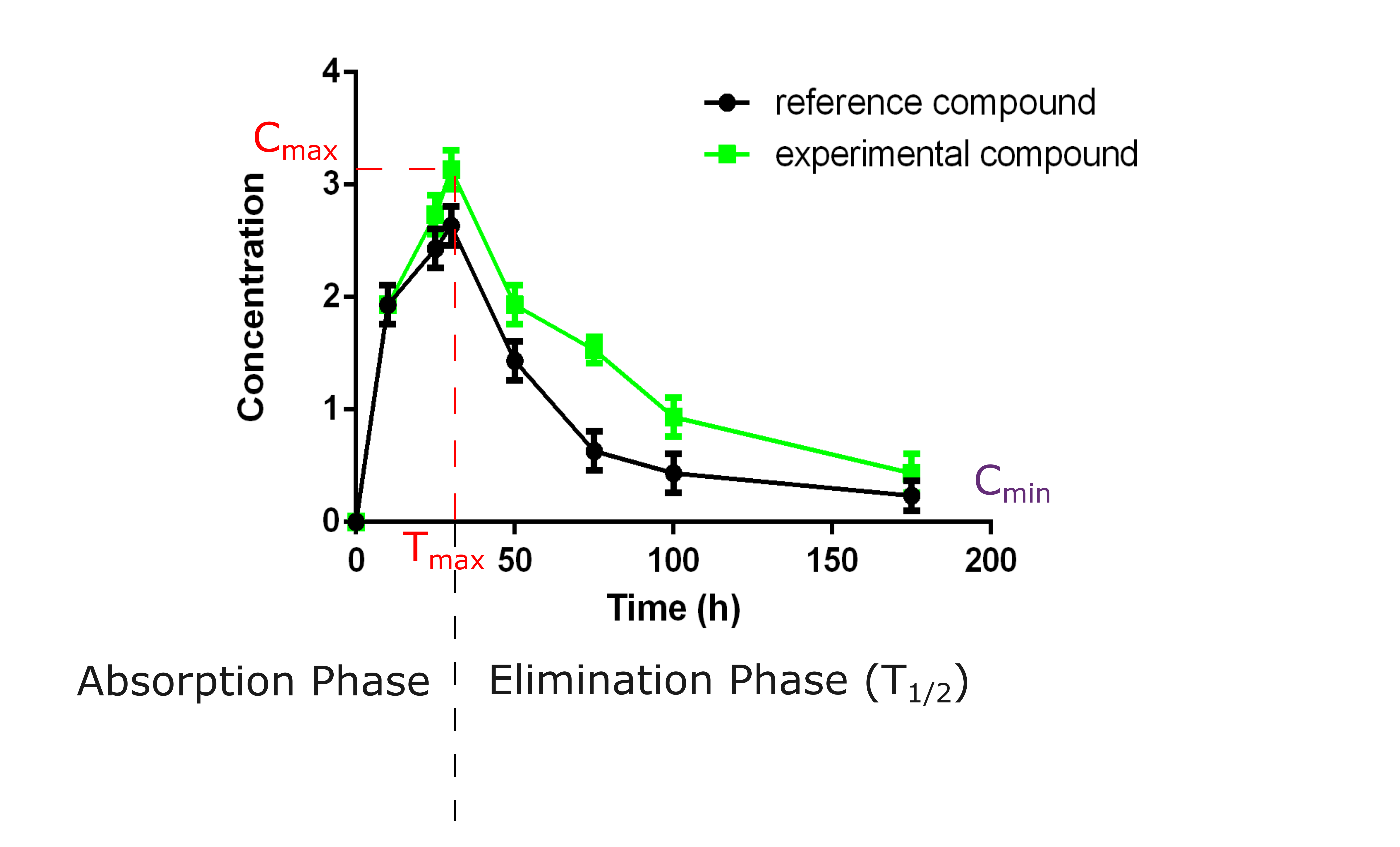
UCL PK/PD Course April 11 25 • " what the body does to the drug what the body does to the drug " • the fate of the drug in terms of – Absorption – Distribution – Metabolism – Excretion • the time course of drug and metabolite concentrations in the body What is pharmacokinetics ?13 Pharmacokinetics I Describe the physicochemical and physiological factors that influence the absorption of drugs from enteral and parenteral routes of administration, their distribution within the body, and their routes and mechanisms of elimination Explain how dose, bioavailability, rate of absorption, apparent volume of distributionPharmacokinetics (PK) describes how the concentration of a dosed drug and its metabolites in body fluids and tissues changes with time PK models the concentrationtime profile using key parameters, such as volume of distribution (V d), area under the curve (AUC), clearance (CL), halflife (t 1/2), maximum concentration (C max), and



Pharmacokinetics Part One




Pharmacokinetics And Biodistribution Of Thymoquinone Loaded Nanostruct Ijn
Http//wwwhandwrittentutorialscom This tutorial is the first in the Pharmacokinetics series It introduces the the four elements (ADME) of pharmacokineti a t1/2 = 0693 Ke b t1/2 = 0693 / Ke c t1/2 = 0693 × Ke d t1/2 = 0693 – Ke Answer b 24 The constants that represent reversible transfer of drug between compartments are called as a microconstants b macroconstant c Infusion d Lag time Answer a 25 In two compartment model, extravascular route of drug administration, therePharmacology Exam 2Pharmacokinetics Only EMU NURS 270 Pharmacology Exam 2 Chapters 15, 27, 28, 51 STUDY PLAY Epinephrine Pharmacokinetics Absorption SQ, IM, IV rapidly;



Back To Basics Pharmacokinetics The Pharmaceutical Journal




Pharmacokinetics Of Drugs Following Iv Bolus Iv Infusion And Oral Administration Intechopen
A Peak at PK ± An Introduction to Pharmacokinetics Hannah Twitchett, Roche Products Ltd, Welwyn Garden City, UK Paul Grimsey, Roche Products Ltd, Welwyn Garden City, UK ABSTRACT The aim of this paper is to give a high level introduction into pharmacokinetic (PK) data and analysis for programmers new to PK, or who require a refresherDescription Nitroglycerin is a vasodilatator used for the treatment of anginal attacks Nitroglycerin decreases the smooth muscle tonus of blood vessels, mainly of the veins, through the local production of nitrous oxide (NO) Nitroglycerin is very liposoluble and is readily transported through membranes Therefore, nitroglycerin is totallyThe T1/2 that is usually reported is the betaphase (bp) T1/2 Ninetyfour percent of any drug's dose will have been eliminated after four bpT1/2s, and about 99% of the drug will have been eliminated after 66 bpT1/2s



Principles Of Pharmacokinetics Chapter 5 Anesthetic Pharmacology



Total Intravenous Anesthesia From Pharmaceutics To Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek pharmakon "drug" and kinetikos "moving, putting in motion";What Medicines Do to the Body Clinical pharmacokinetics is the application of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles to the safe and effective therapeutic management of an individual patient HalfLife Formula The pharmacokinetic term halflife (t1/2) refers to the time taken for half the initial dose of medicine administered to be eliminated from the bodySee chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determine the fate of substances administered to a living organism The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food



2



2
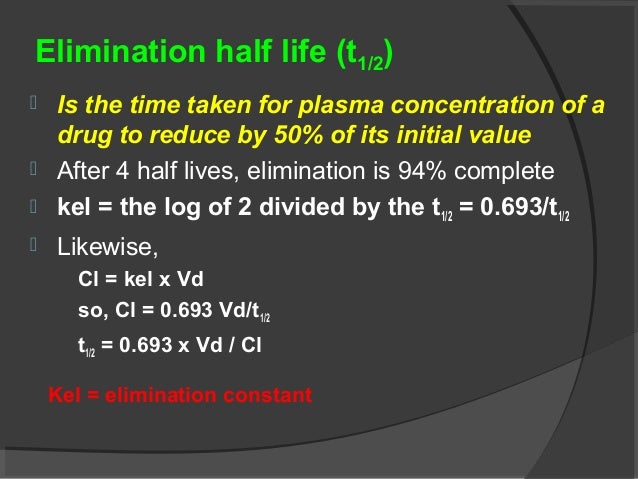
Pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacokinetics 2 Define pharmacodynamics and relate it to pharmacokinetics 3 Describe the concept of the therapeutic concentration range 4 Identify factors that cause interpatient variability in drug disposition and drug response 5 Describe situations in which routine clinical phar Basic pharmacokinetics, k,, t1/2, AUC,AUMC, Vd, Cl, IV /Oral one & two compartment Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website In pharmacokinetics, our perspective is decay with a T1/2 instead being the time required for the amount of drug to decrease by onehalf or 50% The concept of T1/2 is applicable only to firstorder rate processes Using Equation 37, one can derive a simple equation for T1/2




Pharmacokinetics Flashcards Quizlet




Drug Half Life Explained Calculator Variables Examples
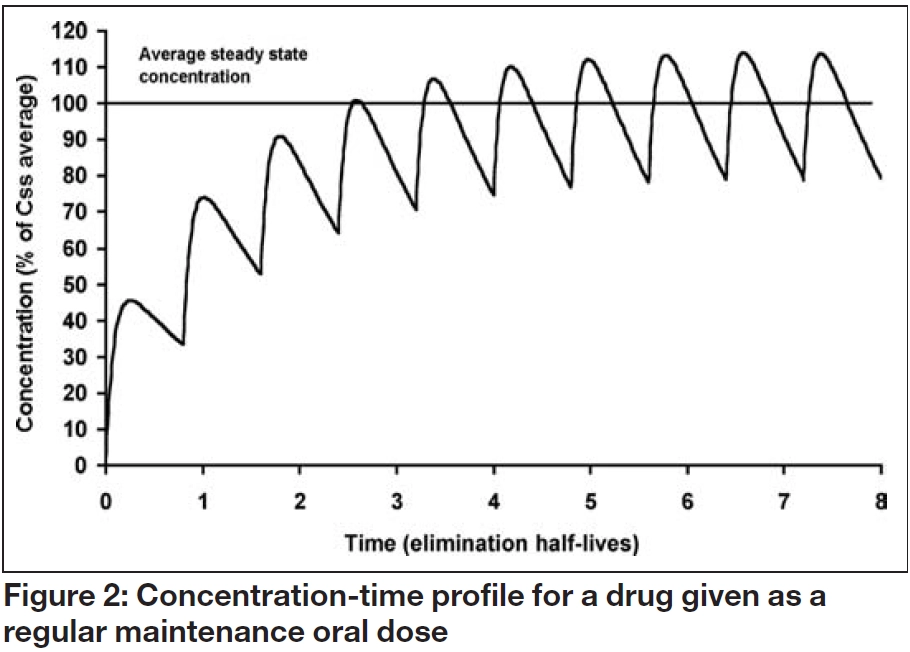
Basic pharmacokinetics (PK) knowledge and skills are essential in practicing therapeutics dose 3, 4, 5,, N1), and so on As a result, after 4 × t 1/2 to 5 × t 1/2 from the first dose of the repeated dosing regimen, there is no substantial difference in the average serum concentrations from dose N to the next dose This is a steady stateIn a drug discovery environment, reasonable go/nogo humaninvivo pharmacokinetic (PK) decisions must be made in a timely manner with a minimum amount of animalinvivo orinvitro data We have investigated the accuracy of theinvivo correlation between rat and human for the prediction of the total systemic clearance (CL), the volume of distribution at steady state (Vss), and the halflife (t1 1/2 changes in direct proportion to Vd Increase in Vd results in a proportional increase in t 1/2 and vice versa Change in Vd does not lead to change in AUC 0 400 800 10 0 4 8 12 16 24) V = 5 L/kg Time (h) Decrease in V d V = 1 L/kg Relationship of Vd with Protein Binding V dss can be related to true physiologic volume Where, V p plasma




Chapter 22 Pharmacokinetics Of Multiple Dosing Handbook Of Basic Pharmacokinetics Including Clinical Applications 7th Edition Pharmacylibrary




Pharmacokinetics Of Drugs Following Iv Bolus Iv Infusion And Oral Administration Intechopen




Six Simple Pharmacokinetic Formulae Download Table




Http Www Speedlighter Cawhyishootstillscourtneycraigphotobymichaelwillems Pharmacokinetics Web Quest Kimberly




Introduction To Pharmacokinetics Tusom Pharmwiki



Preclinical Pharmacokinetic Evaluation To Facilitate Repurposing Of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Nilotinib And Imatinib As Antiviral Agents Bmc Pharmacology And Toxicology Full Text




Evaluation Of The Pharmacokinetic Interaction Between Lobeglitazone And Dapagliflozin At Steady State Clinical Therapeutics




Phar7633 Chapter 21 Page 4



2




A Phase 0 Trial Of Ribociclib In Recurrent Glioblastoma Patients Incorporating A Tumor Pharmacodynamic And Pharmacokinetic Guided Expansion Cohort Clinical Cancer Research




Pharmacokinetics Veterian Key




Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Pharmacokinetics Pharmacology Medbullets Step 1




Pharmacokinetic Calculations Flashcards Quizlet



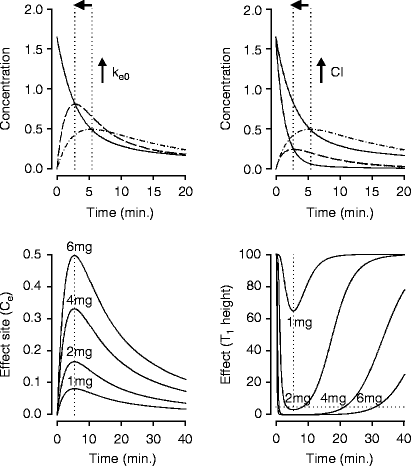
Effect Site Equilibration Deranged Physiology



Ppt Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Plos One The Pharmacokinetics Of Dexmedetomidine In Patients With Obstructive Jaundice A Clinical Trial



Preclinical Non Reglementary Pharmacokinetics Antineo



2




A Randomised Single Blind Single Dose Three Arm Parallel Group Study In Healthy Subjects To Demonstrate Pharmacokinetic Equivalence Of Abp 501 And Adalimumab Annals Of The Rheumatic Diseases




Noncompartmental Vs Compartmental Pk Analysis




Pharmacokinetics And Pharmacodynamics Of Inhaled Corticosteroids Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
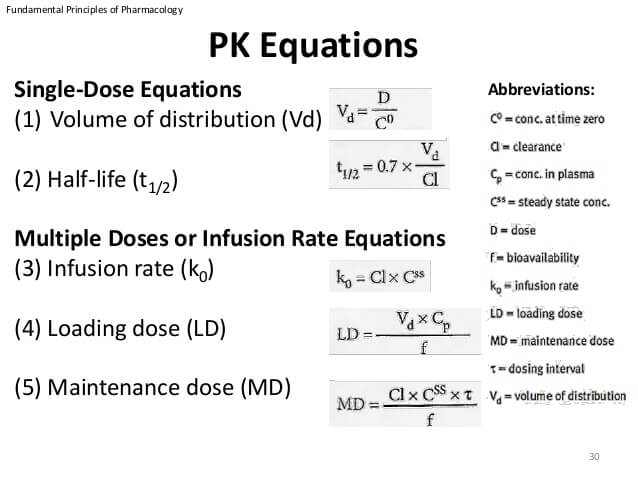



Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics Epomedicine
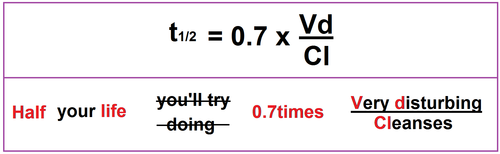



My Notes For Usmle Pharmacokinetics Formulas Mnemonic




Calculated Pharmacokinetic Parameters T1 2 Half Life Vd F Apparent Download Table




Pharmacokinetic Interaction Study Of Ketamine And Rhynchophylline In Rat Plasma By Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
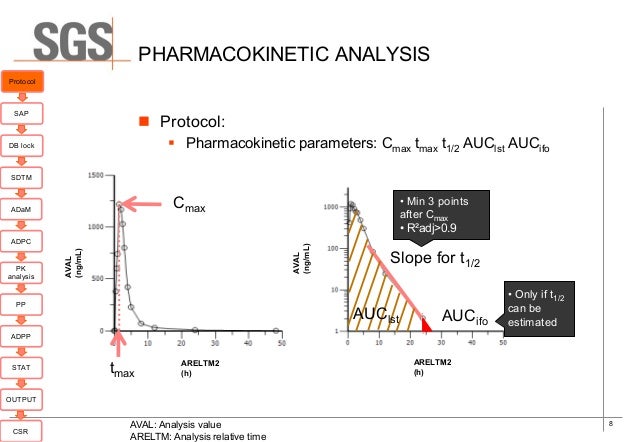



Implementation Of Cdisc Adam In The Pharmacokinetics Department



2



Total Intravenous Anesthesia From Pharmaceutics To Pharmacokinetics




Pharmacokinetics Part Ppt Video Online Download



2




Pharmacokinetic Pharmacodynamic Modeling Of Opioids Journal Of Pain And Symptom Management




Pharmacokinetics Sciencedirect




Chapter 22 Pharmacokinetics Of Multiple Dosing Handbook Of Basic Pharmacokinetics Including Clinical Applications 7th Edition Pharmacylibrary



2
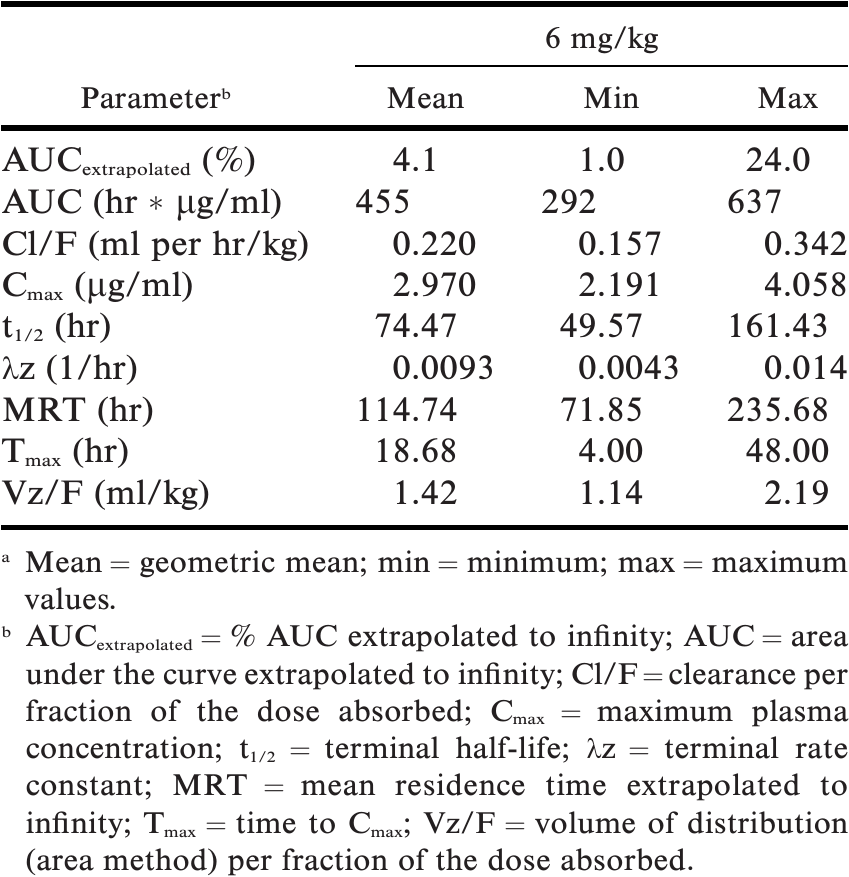



Pharmacokinetics Of Oral Mavacoxib In Caribbean Flamingos Phoenicopterus Ruber Ruber



2



Back To Basics Pharmacokinetics The Pharmaceutical Journal



2



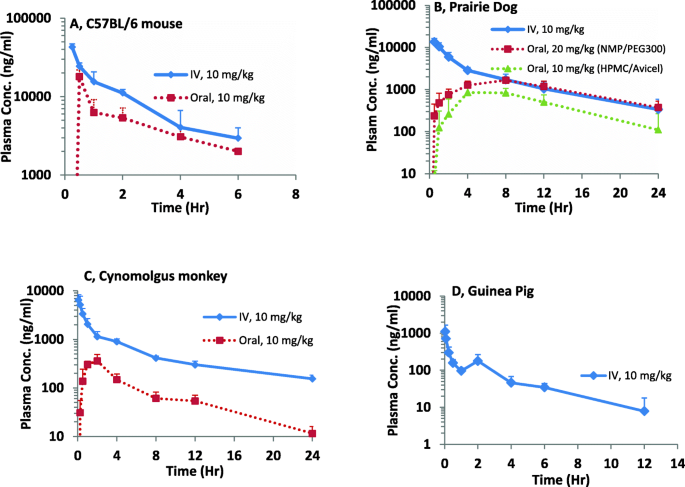
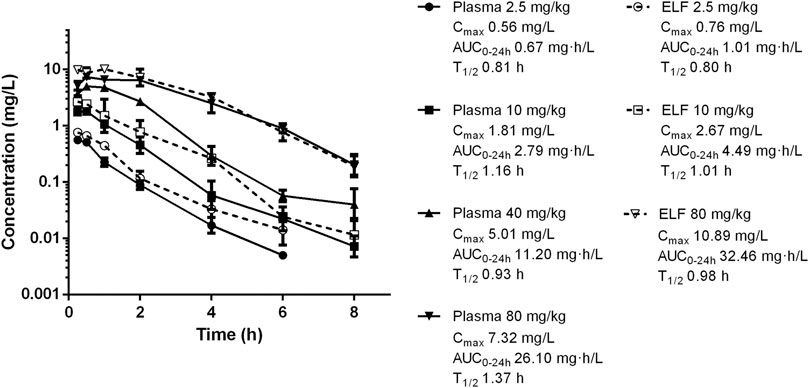
Frontiers An In Vitro Adme And In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study Of Novel Tb Active Decoquinate Derivatives Pharmacology




Pharmacokinetics Veterian Key



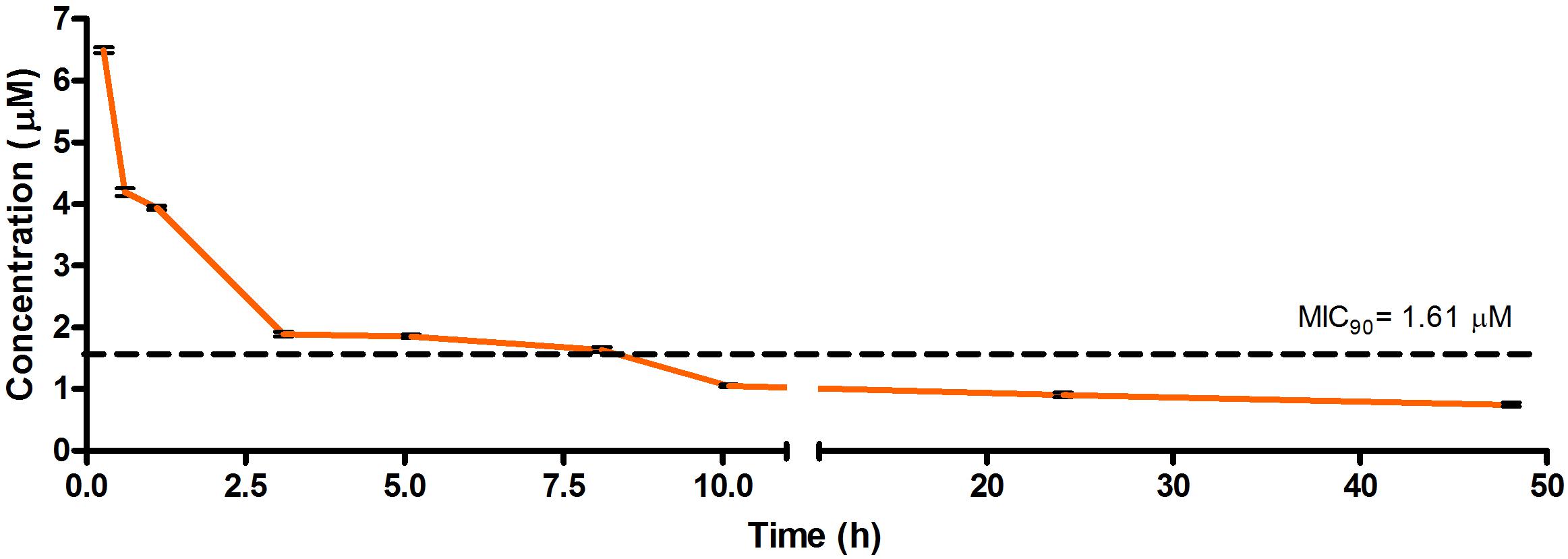
Frontiers Pharmacokinetics And Pharmacodynamics Of Nemonoxacin In A Neutropenic Murine Lung Infection Model Against Streptococcus Pneumoniae Pharmacology



Plateau Principle Pharmacology




A Method To Determine Pharmacokinetic Parameters Based On Andante Constant Rate Intravenous Infusion Scientific Reports
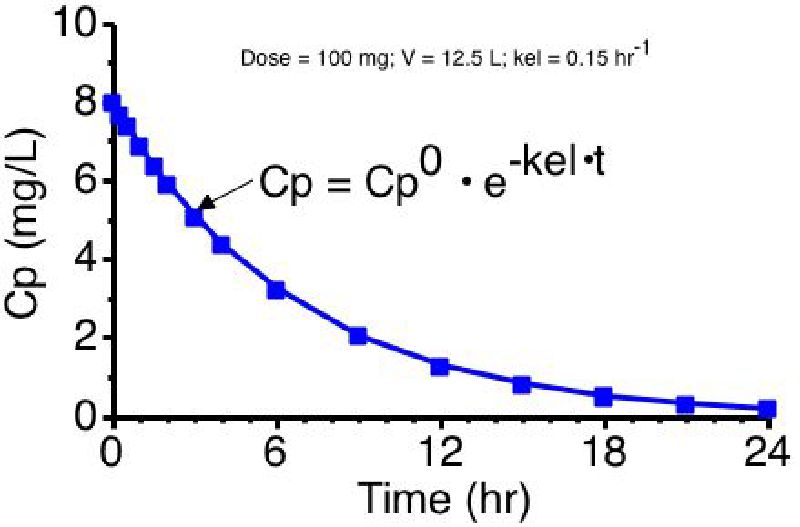



Pharmacokinetics Of Drugs Following Iv Bolus Iv Infusion And Oral Administration Intechopen




Pharmacokinetics Video 2 Kel And Half Life Youtube



2
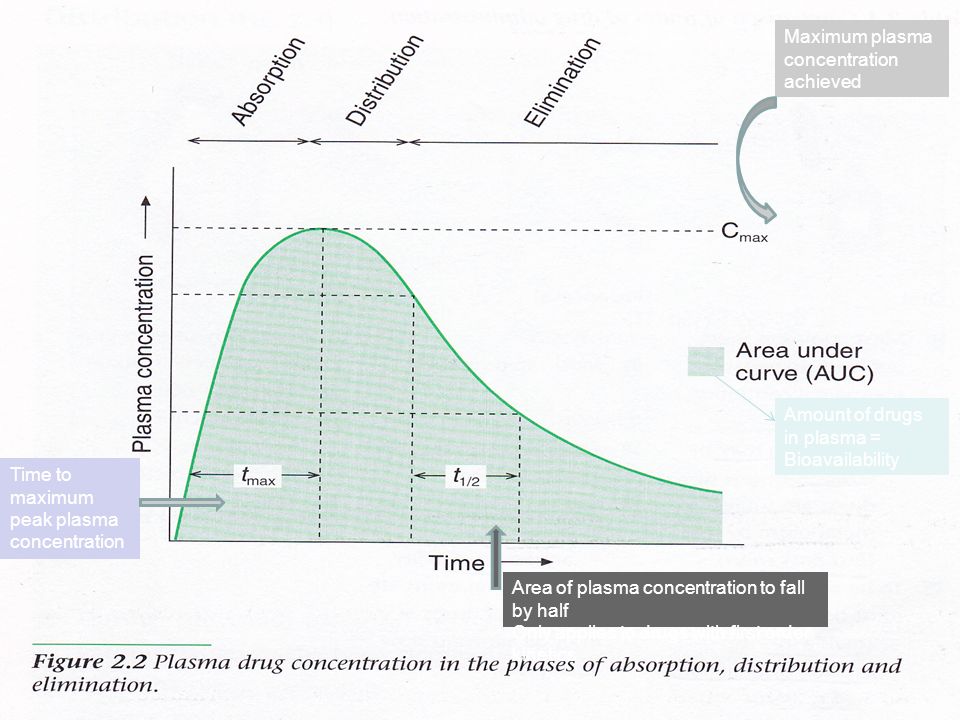



Definitions T1 2 Tmax Cmax Auc 1st Order Kinetics Ppt Video Online Download



2
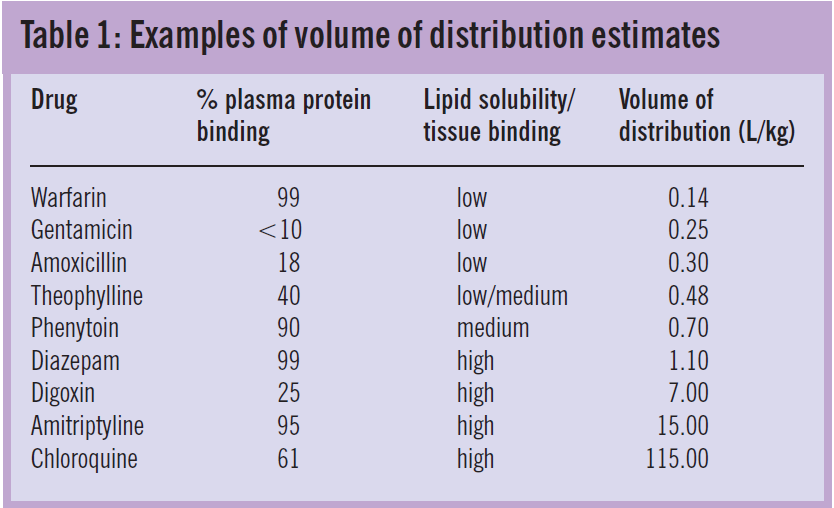
/N.Davies/Table1.gif)



Formulation Dependent Pharmacokinetics Bioavailability And Renal Toxicity Of A Selective Cyclooxygenase 1 Inhibitor Sc 560 In The Rat



2




Chapter 4 Page 10




Kaplan Usmle Step 1 Prep What S Half Life Of Investigational Drug American Medical Association




Clinical Pharmacokinetics In Kidney Disease American Society Of Nephrology




Pharmacokinetics And Pharmacodynamics Ausmed




Difference Between Tmax And T1 2 Peak Plasma Time Vs Elimination Half Life




Pdf Comparative Allometric Analysis Of Pharmacokinetics Of Florfenicol And Tiamphenicol Semantic Scholar
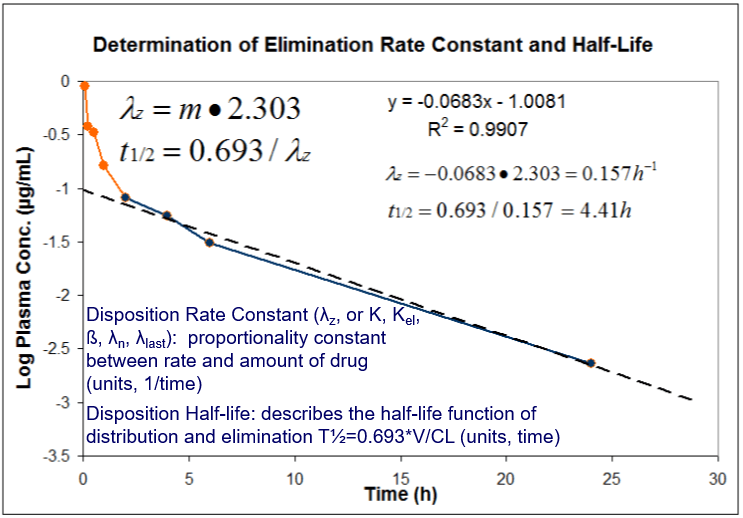



Pharmacokinetics Pk Pharmacodynamics Pd Pk Pd Northeast Biolab



2




Nefazodone Pharmacokinetics In Depressed Children And Adolescents Journal Of The American Academy Of Child Adolescent Psychiatry
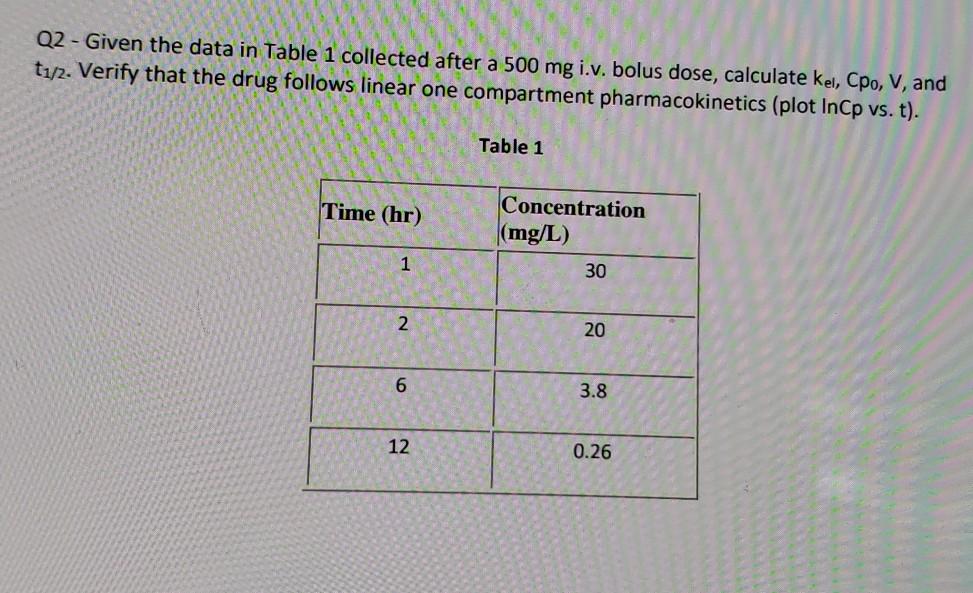



Q2 Given The Data In Table 1 Collected After A 500 Chegg Com



2



2



Plos One Pharmacokinetics And Bioequivalence Of Two Formulations Of Febuxostat 40 Mg And 80 Mg Tablets A Randomized Open Label 4 Way Crossover Study In Healthy Chinese Male Volunteers




Pharmacokinetics Wikipedia



Pharmacokinetics Part One



1



2
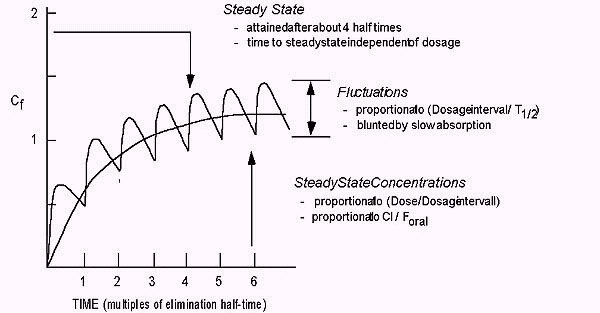



Pharmacokinetics




Pharmacokinetics Wikipedia



Effect Site Equilibration Deranged Physiology



2



2
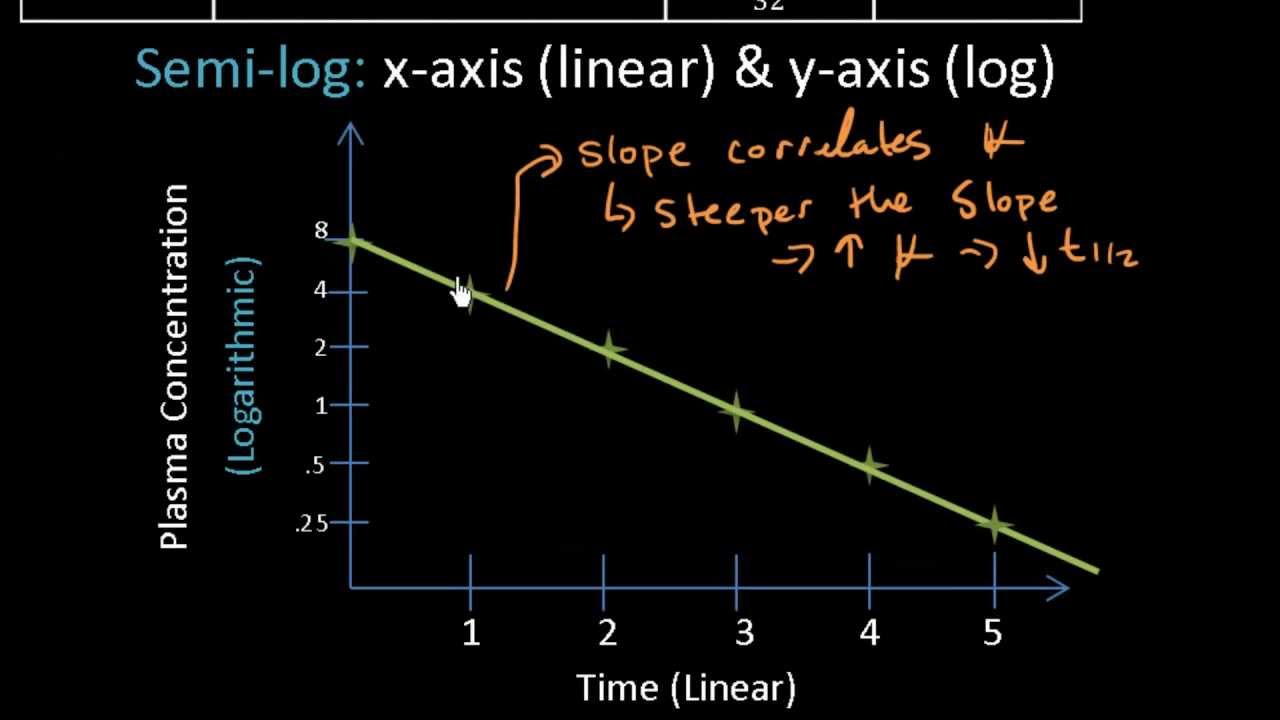



General Principles Of Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics



Plos One Single Oral Dose Pharmacokinetics Of Decursin And Decursinol Angelate In Healthy Adult Men And Women




Kaplan Usmle Step 1 Prep What S Half Life Of Investigational Drug American Medical Association




Pharmacokinetics And Pharmacodynamics Ausmed




Pharmacokinetics Of 18f E4tz12 7 A Blood Half Life T1 2 Weighted Download Scientific Diagram




Clinical Pharmacokinetics In Kidney Disease American Society Of Nephrology




Effect Of Food And Multiple Dose Pharmacokinetics Of Tmc278 As An Oral Tablet Formulation Healthy Volunteers



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿